ADADVESHI
Botanical Name: Tylophora indica ( ASCLEPIADACEAE)
English Name: Indian ipecac
Hindi Name: Antmool, Jangli pikvan
Introduction: It is traditionally used as a folk remedy in certain regions of India for the treatment of bronchial asthma ( Bielory & Lupoli, 1999), inflammation (Exoticnatural. 2005), bronchitis, allergies, rheumatism and dermatitis ( Gupta & Bal, 1956; Shivpuri et al., 1969; Dhananjayan et al.,1974; Mathew and & Shivpuri, 1974; Haranath & Shyamalakumari, 1975; Thiruvengadam et al., 1978; Gupta et al;l 1979; Karnick and Jopat, 1979; and Gore et al., 1980; True star health, 2005; Remedyfind, 2005). Apart from the above, it is a good remedy as anti-psoriasis, seborrheic, anaphylactic, leucopenia and asa an inhibitor of the Schultz-Dale reaction (Sarma, 1978, Sarma & Misra, 1995). It is said to have laxative, expectorant, diaphoretic and purgative properties. It has also been used for the treatment of allergies, cold, dysentery, hay fever and arthritis ( CSIR, 1948-1976).
Distribution: Perennial, small, slender, much branched pubescent twining or climbing herbs or under shrubs. Found in north and eastern Bengal, Assam, Orissa and cultivated in gardens.
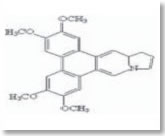
Chemical Constituents: Tylophorine and tylophorinine are the major constituents in this plant. The other alkaloids include Tylophorinidine, Septicine and Isotylocrebrine.
Parts Used: The leaves and roots are used medicinally (Bhavan, 1992).
Properties: bitter, stimulant, emetic, cathartic & purgative, anti- inflammatory, antiallergic, and antispasmodic, alternative, blood purifier, expectorant, anti tumour etc.
Indications: rheumatism, syphilitic rheumatism, diarrhea, dysentery, intermittent fever, hydrophobia.
Dose: According to Bone (1996), the dose should not exceed 200-400 mg dried leaf powder per day or 1 to 2ml of tincture per day for the treatment of asthma.
Therapeutic Uses:
- Asthma: Tylophora leaf chewed and swallowed daily in the early morning for six days reduces asthma symptoms.
- The roots are suggested to be a good natural preservative of food.
Scientific Studies:
Anti-inflammatory activity: Tylophorine exhibited anti-inflammatory activity (Gopalakrishnan et al., 1980). The plant shows inhibitory effect on cellular immune response ( Ganguly & Sainis, 2001) and antiallertic activity ( Nayampalli & Sheth, 1979).
Anti-asthmatic activity: Tylophora leaf chewed and swallowed daily in early morning for 6 days reduced asthma symptoms (Shivpuri et al., 1969). An alcoholic extract of crude Tylophora leaves in 1 gram of glucose had comparable effects to that of chewing the crude leaf (Shivpuri et al., 1972).
Cultivation Technology: The plant is well suited to loam to sandy-loam soils. It is propagated through stem cuttings or suckers, which comes near to the base of mother plants. 10-15 cm long stem cuttings with atleast 2-3 internodes are planted in poly bags in the month of June-July. Rooted stem cuttings/ detached suckers are planted to the field at the distance of 30x30 cm. As the plant is a weak climber, so require proper staking to climb. Irrigate the field after planting and later as and when required.
Harvesting: Mature leaves are collected.








